There is a difference between the expiration date on your visa and how long you are authorized to stay in the United States. It is important to understand this difference as a NIH foreign national scientist. Review the guidance below regarding visa vs. status.
What is a “visa"?
A
visa is a sticker placed inside of your passport by a U.S. Consulate or Embassy. A visa is a travel document used to request entry into the United States. The validity dates on the visa mean you can request entry to the United States during those dates. Your visa can expire once you are inside the United States since it is a travel document. Review the
U.S. Department of State website for additional guidance.
What is “status"?
Your immigration
status is the legal category that you were granted either 1) when you entered the United States or 2) when the U.S. Citizenship & Immigration Services (USCIS) approved a petition or application on your behalf.
Your most recent
Form I-94 reflects your current immigration status. If USCIS approved a petition or application on your behalf since the last time you entered the United States, your most recent I-94 is located on the bottom left corner of your Form I-797 Approval Notice.
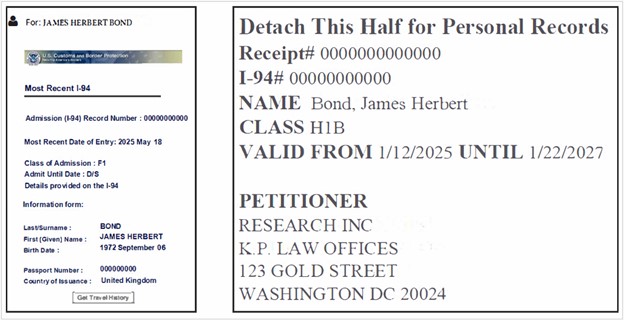
When does my status expire?
You are authorized to remain in the United States through the expiration date on your most recently issued I-94 record. In most cases, the expiration or “admit until" date on Form I-94 will list a specific status end date.
If you are in F-1 or J-1 status, as long as your most recent Form I-94 lists the admit until date as “D/S" (duration of status) and you have a valid enabling document (Form DS-2019 or Form I-20), you are permitted to stay in the United States until the end date on your enabling document. If your DS-2019 or I-20 is renewed, you can stay until the new end date.
Certain immigration statuses have a “grace period," which allows you to remain in the United States – but not work – for a limited period at the end of your time at NIH. For example, J-1 Exchange Visitors have an automatic 30-day grace period at the end of their NIH program. Grace periods are not automatically granted for all immigration statuses. Contact DIS if you have additional questions.
You must follow all the rules and regulations associated with your status. If you violate any of these regulations, you may be considered “out of status", meaning you no longer have a lawful basis for being in the United States.
How can I renew my status/extend my stay at NIH?
For J-1/H-1B scientists, refer to our
Extending Your J-1 Program and
H-1BOverview pages.
For all other scientists, please work with your Administrative Officer to either submit a
renewal case or updated immigration documents to DIS.
What happens if my visa expires?
If your visa expires in the United States, it will not affect your immigration status. However, if your visa expires and you leave the country, you will most likely need to renew your visa before returning to the United States. Certain nonimmigrants traveling to Canada, Mexico, or an adjacent island for 30 days or less may be eligible for
automatic visa revalidation.
How can I renew my visa?
You can only apply for a visa at an Embassy or Consulate outside of the United States. Applicants should schedule their visa interview appointments at the
U.S. Embassy or Consulate in their country of nationality or residence. Refer to the
DIS guidance on visa renewal for your immigration status. Contact the specific
Embassy or Consulate for procedures.
Can I renew my visa in the United States?
Unfortunately, a visa cannot be renewed within the United States. Only a U.S. Consular Officer at a U.S. Embassy or Consulate has the authority to issue visas for travel to the United States. See the U.S. Embassy website to find the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate in your home country.
How long will my visa be valid for?
The validity of a visa depends on
reciprocity agreements between the United States and your home country. It is also subject to the discretion of the U.S. Consular Officer. The visa validity and number of entries will vary. Remember, visa validity dates are often different than status validity dates.
